The logistics industry is one of the most expansive and influential fields today, and it is also one of the oldest, with records of the profession dating back to the 2nd century AD. The field has grown and changed over time to what it is today, with technology continuing to play a crucial role in operations. With the rise of robotic systems and artificial intelligence, the logistics industry is seeing another wave of change affecting how it operates moving forward. Various new technologies are revolutionizing this field, from autonomous drones and self-driving trucks to collaborative robots and warehouse automation software.
Development of Automated Guided Vehicles
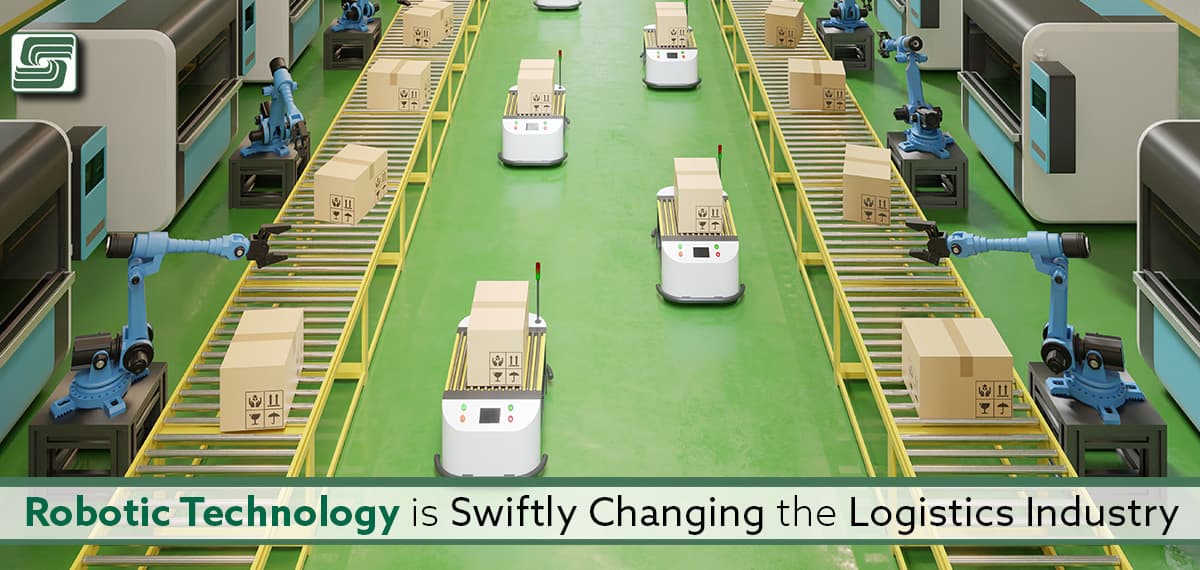
Automated guided vehicles (AGV) is an automated guided vehicle used in the logistics field for decades originally built for mining operations but has changed for other industries, including logistics. AGVs follow a set path programmed into the system, moving along a track with sensors that guide them along the route and prevent collisions with obstacles. Various industries, such as manufacturing, food and beverage, and pharmaceutical industries, use AGVs. They're also used in logistics operations involving transporting finished goods from one place to another.
Self-Driving Vehicles
The rise of autonomous vehicle technology is affecting more than just the automobile industry. Autonomous vehicles, or AVs, transport goods in logistics operations while functioning in many ways, including on water, air, and road. The logistics industry uses AVs in various applications, including transporting raw materials, finished goods, and cargo. Autonomous vehicles also move people using ride-sharing services. The benefits of autonomous vehicles in logistics operations include reduced emissions, improved safety, and lower operational costs. AVs will significantly influence the global economy, as they could increase productivity and enable countries to become more competitive with lower costs: good news for businesses, customers, and the environment at large.
Robotics in Warehousing
Robotics is another technology heavily used in the warehousing and storage industry. It is an automated process involving machines to perform tasks usually done by humans, including picking and packing orders for machine maintenance. Warehouses typically use robotics for repetitive tasks to maximize efficiency and reduce the risk of human error, including activities like lifting and moving products, placing orders, and organizing inventory. Robotics technology automates various functions, including picking and packing orders, machine tending, and order sorting. Order picking is one of the most common implementations of robotics and has been used in different ways over the years. Warehouse automation software is another robotics practice that is increasing in popularity.
Collaborative Robotics
While most people associate robotics with machines doing work autonomously, collaborative robotics is a different type of technology that involves humans and robots working together. Collaborative robots work with human coworkers, often used for simple tasks requiring high precision. Collaborative robots work alongside humans in the workplace and are safe to work around, often used in logistics, helping pack and unpack orders, assembly, and more. Some of the most common collaborative robots include the Sawyer robot by Rethink Robotics, the UR5 by Universal Robots, and the YuMi robotic arm by ABB.
Automated Warehouse Robots
The logistics industry uses automated robots to automate tasks, such as assembly or material handling. Manufacturing plants have used this technology for decades, but only recently implemented it in logistic operations. Programmed with precise instructions for tasks, automated robot systems perform precise tasks accurately, often used with other technologies, such as sensors, material handling equipment, and robotic arms. The logistics industry uses automated robots for diverse applications, including palletizing, packaging, sorting, and picking orders. Some of the most common types of automated robots include AGVs, robotic arms, automated guided vehicles, and autonomous vehicles.
Automated Guided Vehicle Advantages
There are a variety of advantages to using automated guided vehicles in logistics operations, including reduced maintenance costs, lower energy consumption, and minimized risk of injury to humans. AGVs also reduce accident risk because their programming tells them to follow the directed paths and recognize and avoid obstacles. Most automated guided vehicles also have several sensors, including cameras and laser scanners, that help them navigate along the path and avoid obstacles and other AGVs in the area. They can implement this technology on a small or large scale, making it a versatile option for different operations.
Automated Guided Vehicle Limitations
While automated guided vehicles are very beneficial, there are a few limitations to keep in mind, including their inability to adapt to environmental changes, reliance on a power source, and potential for mechanical malfunctions. We program automated guided vehicles to follow specific paths, but they can't adapt to changes occurring along the way. In other words, the system can't change if the path changes. This technology also requires a power source, such as an overhead track or rechargeable batteries, which create issues in certain scenarios. For example, the system will be inoperable during a power outage with drained batteries. Finally, since automated guided vehicles are mechanical systems that can break down, they can be susceptible to mechanical malfunctions.
Looking Forward to AGV Advances
While automated guided vehicles have seen a lot of use in the past, they are likely to see even more growth in the future as technology continues to advance. One expected area of change is the AGV design. While their current design leaves them large and bulky, confined to tracks, newer, smaller versions may navigate environments without needing tracks.
AGVs may also include:
- Wireless communication.
- Enabling them to communicate and collaborate.
- Improving their ability to navigate complex environments and potential obstacles.
In Sum
The logistics industry is a complex network of activities essential to any company's operation. From transporting raw materials to delivering finished goods, logistics operations are essential to businesses across industries. Robotics technology plays a key role and helps revolutionize things from end to end.